How to Distinguish Heat Exchangers from Condensers
On this page
Condenser and heat exchanger are important heat transfer devices in modern industry. Condensers play an important role in refrigeration, air conditioning and industrial cooling by rapidly cooling high-temperature gases or vapors, converting them into liquids and efficiently releasing heat. Heat exchangers, on the other hand, optimize heat transfer through various structural designs and are widely used in heating, cooling and energy recovery processes in the chemical, power generation and petroleum industries. These devices are essential for optimizing energy efficiency and process control. Below, we will comprehensively explore the functions and applications of condensers and heat exchangers.
The Basic Function of Condenser
Condensers are specifically designed to quickly cool gases or vapors, turning them into liquids. They work by transferring heat to the cooling medium (usually water or air), so that the high temperature and high pressure steam condenses into a liquid after contact with the cooling medium at a lower temperature. Condensers are typically constructed in tube or plate configurations to maximize heat transfer surface area and efficiency to ensure effective heat transfer. In refrigeration, air conditioning, cold storage and industrial cooling systems, condensers play a key role by releasing heat to achieve the cooling effect of space and objects.
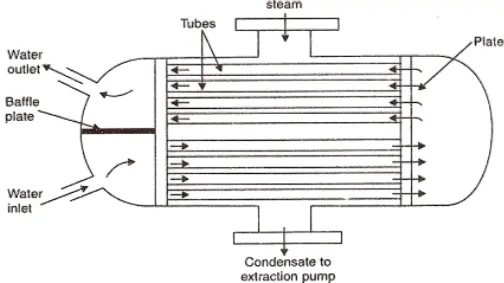
The Main Application of Condenser
As an important heat transfer device, the condenser is mainly responsible for rapidly cooling the gas or steam into a liquid state. These devices are critical in many applications.
1. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems
In the refrigeration cycle, the condenser converts high-temperature and high-pressure steam into a liquid, releasing a large amount of heat. This process allows the air conditioning system to effectively remove heat from the indoor air, thereby reducing the indoor temperature.
2. Industrial Cooling Application
In industrial processes, many operations produce high-temperature steam or gases. The condenser quickly cools these thermal media to ensure the stable operation of production equipment and processes. For example, condensers are often used to cool hot gases produced in chemical reactions, or to handle vapors from refrigerants such as liquid ammonia and freon.
3. Heat Recovery
The condenser also contributes to the heat recovery system, transferring the recovered heat to other media to improve energy efficiency. For example, in a cogeneration plant, a condenser recovers heat from exhaust gases during power generation for heating or other industrial uses.
4. Cold Chain Logistics and Cold Storage
In industries such as food, pharmaceuticals and chemicals, maintaining a cold environment is crucial to maintaining freshness or storing specific medicines. The condenser helps maintain a constant temperature in these environments, ensuring product quality and safety.
The Main Function of Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger uses the heat exchange principle between two fluids to regulate the temperature and transfer energy, thereby promoting the heat transfer between different fluids. Heat exchangers are designed in a variety of shell and tube, plate and coil configurations to provide a compact and efficient solution for a variety of process requirements. Heat exchangers are widely used in chemical, power generation, petroleum, metallurgy and other industries, is an indispensable equipment in the process of heating, cooling, evaporation, condensation, etc., with flexibility and high energy utilization efficiency.
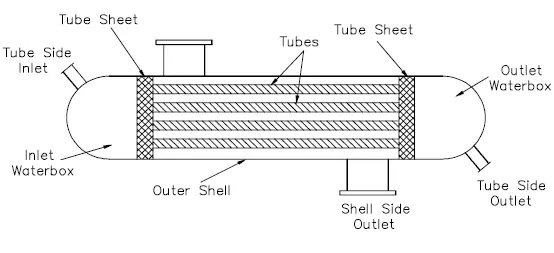
Common Applications of Heat Exchangers
As key heat transfer equipment, heat exchangers have a wide range of applications in industrial and commercial environments.
1. Chemical Industry
In the chemical production process, heat exchangers are used as part of heaters, coolers or reactors to facilitate temperature control and optimize the efficiency and quality of chemical reactions.
2. Electric Power Industry
Power plants use heat exchangers to cool the cooling medium in generators and other equipment to improve power generation efficiency. The heat exchanger also recovers waste heat from the boiler system for heating water or generating steam.
3. Oil and Gas Processing
In petroleum refining and natural gas processing, heat exchangers handle high temperature media such as petroleum products and chemical gases, facilitating the cooling or heating of these fluids at different stages of processing.
Condensers and heat exchangers play different but crucial roles in industrial applications. Condensers focus on rapidly cooling a gas or steam into a liquid, releasing heat to achieve a cooling effect, while heat exchangers optimize heat transfer through a variety of designs and structures and are widely used in heating, cooling and energy recovery processes. Their differences in design and application determine their unique contribution to industrial production, providing critical support for improving energy efficiency and process control.

