Four Inquiries Regarding Heat Exchangers
1. How to Compare the Indicators of Heat Exchange Equipment?
Different types of heat exchange equipment can be compared based on factors such as high efficiency, compact structure, material savings, low pressure drop, reliable structure, low manufacturing cost, easy installation, maintenance, and long service life.
2. How to Describe the Model of a Heat Exchanger?
DN represents the nominal diameter of the heat exchanger, indicating the inner diameter of the rolled cylinder and the outer diameter of the steel cylinder. A is the nominal heat exchange area based on the outer diameter of the heat exchange tube. LN is the nominal length, referring to the length of the heat exchange tube. S is the type of heat exchange tube (specific to aluminum, copper, titanium). Pt/ps represents the design pressure of the tube/shell side. Class I tube bundles use higher-level cold-drawn heat exchange tubes, suitable for non-phase change heat transfer occasions with minimal vibration. Class II tube bundles consist of ordinary cold-drawn heat exchange tubes, suitable for general applications like reboiling, condensation heat transfer, and no vibration. Classes I and II tube bundles are limited to carbon steel and low alloy steel. The representation method is as follows:
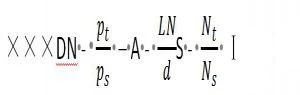
3. What Are the Standards for Selecting a Heat Exchanger?
When selecting a heat exchanger for a specific heat load, the following points should be considered:
(1) Material of the heat exchanger
(2) Changes in operating pressure and temperature
(3) Quantity and type of flow
(4) Performance parameters - thermal efficiency and pressure drop
(5) Fouling tendency
(6) Fluid types and phase states
(7) Possibility of maintenance, inspection, cleaning, expansion, and repair
(8) Overall economy
(9) Manufacturing technology
(10) Other uses
4. How to Select Heat Exchange Equipment?
The selection of heat exchange equipment should adhere to the following principles:
(1) Choose a shell-and-tube heat exchanger for high temperature and high-pressure operations with large handling capacity, prioritizing reliability of strength.
(2) Select a heat exchanger with corrosion-resistant material for highly corrosive fluids.
(3) For conditions with moderate pressure and temperature, and smaller processing capacity, where precious metal materials are needed due to corrosive requirements, consider choosing a plate type heat exchanger (plate type, plate fin type) known for high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, and less metal consumption.
Different types of heat exchange equipment can be compared based on factors such as high efficiency, compact structure, material savings, low pressure drop, reliable structure, low manufacturing cost, easy installation, maintenance, and long service life.
2. How to Describe the Model of a Heat Exchanger?
DN represents the nominal diameter of the heat exchanger, indicating the inner diameter of the rolled cylinder and the outer diameter of the steel cylinder. A is the nominal heat exchange area based on the outer diameter of the heat exchange tube. LN is the nominal length, referring to the length of the heat exchange tube. S is the type of heat exchange tube (specific to aluminum, copper, titanium). Pt/ps represents the design pressure of the tube/shell side. Class I tube bundles use higher-level cold-drawn heat exchange tubes, suitable for non-phase change heat transfer occasions with minimal vibration. Class II tube bundles consist of ordinary cold-drawn heat exchange tubes, suitable for general applications like reboiling, condensation heat transfer, and no vibration. Classes I and II tube bundles are limited to carbon steel and low alloy steel. The representation method is as follows:
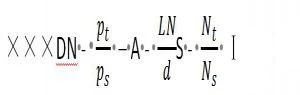
3. What Are the Standards for Selecting a Heat Exchanger?
When selecting a heat exchanger for a specific heat load, the following points should be considered:
(1) Material of the heat exchanger
(2) Changes in operating pressure and temperature
(3) Quantity and type of flow
(4) Performance parameters - thermal efficiency and pressure drop
(5) Fouling tendency
(6) Fluid types and phase states
(7) Possibility of maintenance, inspection, cleaning, expansion, and repair
(8) Overall economy
(9) Manufacturing technology
(10) Other uses
4. How to Select Heat Exchange Equipment?
The selection of heat exchange equipment should adhere to the following principles:
(1) Choose a shell-and-tube heat exchanger for high temperature and high-pressure operations with large handling capacity, prioritizing reliability of strength.
(2) Select a heat exchanger with corrosion-resistant material for highly corrosive fluids.
(3) For conditions with moderate pressure and temperature, and smaller processing capacity, where precious metal materials are needed due to corrosive requirements, consider choosing a plate type heat exchanger (plate type, plate fin type) known for high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, and less metal consumption.

