Comparative Analysis of Pressure Vessels with Different Shapes
On this page
The appearance and shape of pressure vessels vary due to their design and functional requirements, which determine their roles and performance in different industrial applications. As sealed equipment, pressure vessels contain gases or liquids and must withstand certain pressures. Therefore, the design of different pressure vessels concerns not only safety but also economic and operational efficiency.
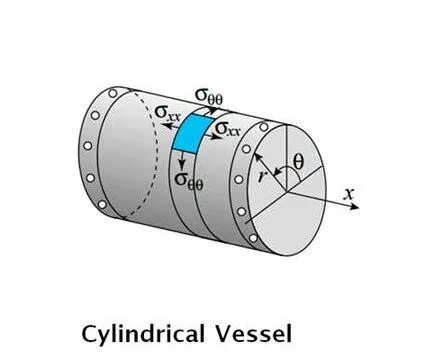
Cylindrical Pressure Vessels
Cylindrical vessels are one of the most common and fundamental types of pressure vessels. Their basic structure includes a cylindrical body, two heads, flanges, sealing elements, openings, pipelines, and internal supports. This shape is easy to manufacture and structurally stable, suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, such as storage and transportation in the oil and chemical industries, and storage of liquefied gases. Advantages of cylindrical vessels include:
- Ease of Manufacture: The cylindrical shape is relatively easy to process and weld in industrial manufacturing, reducing production costs.
- Structural Stability: The cylindrical structure allows for even distribution of internal pressure, enhancing overall stability and durability.
- Versatility: Suitable for storing various liquids and gases, meeting the needs of different industries.
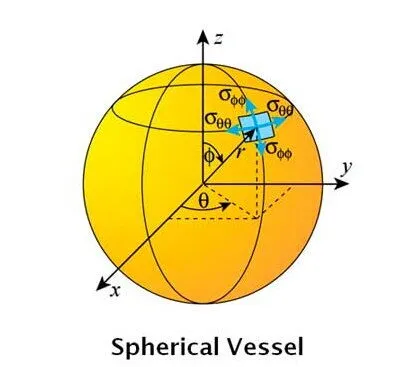
Spherical Pressure Vessels
Spherical vessels, shaped like a sphere, can effectively withstand internal pressure and have excellent mechanical properties and material utilization rates. Compared to cylindrical vessels, spherical containers have a higher load-bearing capacity at the same wall thickness, and due to their shape, they have a relatively smaller surface area, thus saving more steel. Characteristics of spherical vessels include:
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Suitable for storing and transporting gases and liquids that require high pressure, such as liquefied gases and chemical raw materials.
- Material Conservation: Compared to other shapes, spherical vessels can save material costs at the same volume, especially significant for large containers.
- Complex Manufacturing: The manufacturing and construction of spherical vessels are relatively complex, requiring high-precision manufacturing processes and technology, resulting in higher costs.
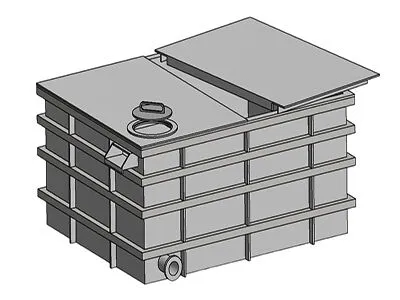
Rectangular Pressure Vessels
Rectangular vessels are typically used for specific low-pressure gas or liquid storage and transportation needs. Although rectangular vessels are relatively less used in some fields, they still play an important role in specific situations. For example, for applications that require special shape adaptability, such as the storage and transportation of sensitive powder materials, rectangular vessels can provide more flexibility and space utilization. Characteristics of rectangular vessels include:
- Structural Stability: For occasions with specific shape requirements, rectangular vessels can provide sufficient stability and structural strength.
- Adaptability: Suitable for applications that require special shapes or sizes, such as the storage and transportation of sensitive powder materials.
Pressure vessels of different shapes each have their advantages and disadvantages in industrial applications, and the appropriate shape and design should be selected based on specific usage requirements and environmental conditions. Cylindrical vessels are widely used due to their versatility and stability, spherical vessels are suitable for occasions with high load-bearing requirements, and rectangular vessels leverage their unique advantages in situations with special shape and space needs. By understanding and selecting pressure vessels of different shapes, various demands in industrial production and transportation can be met to the greatest extent.

